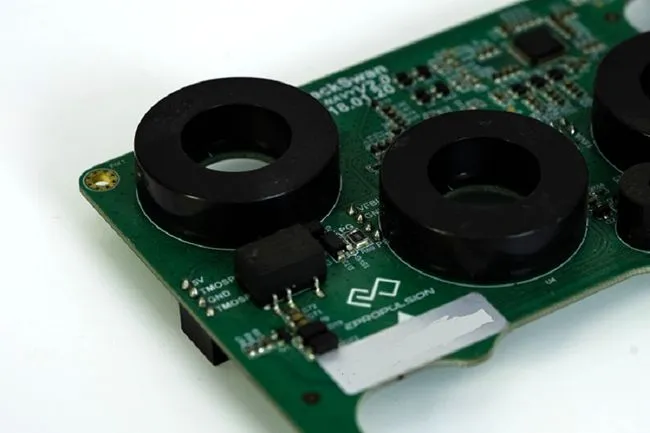
Grasping the Fundamentals of Power PCBA
Power PCBA plays a crucial role in modern electronics, serving as the backbone for energy distribution and management within devices. These specialized circuit boards are designed to handle varying levels of electrical power, from milliwatts in small gadgets to kilowatts in industrial equipment. The primary function of a Power PCBA is to regulate, convert, and distribute electrical energy efficiently throughout a system.
At its core, a Power PCBA consists of various components such as power transistors, voltage regulators, capacitors, and inductors. These elements work in harmony to ensure stable power delivery, protect against voltage fluctuations, and optimize energy usage. The layout and design of a Power PCBA are critical factors that influence its performance, reliability, and safety.
Key Components of Power PCBA
Several essential components make up a Power PCBA:
- Power MOSFETs: These transistors are responsible for switching and controlling high currents.
- Voltage Regulators: They maintain a constant voltage level, protecting sensitive components from fluctuations.
- Filter Capacitors: These components smooth out voltage ripples and store energy for momentary power demands.
- Inductors: They help in filtering noise and storing magnetic energy in switch-mode power supplies.
- Power Management ICs: These integrated circuits oversee various power-related functions, including voltage conversion and battery management.
The careful selection and arrangement of these components are paramount in creating an efficient and reliable Power PCBA. Factors such as heat dissipation, EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) shielding, and proper grounding must be considered during the design phase to ensure optimal performance.
The Importance of Power PCBA in Modern Electronics
As electronic devices become increasingly complex and energy-efficient, the role of Power PCBA has grown in significance. These specialized circuit boards enable the miniaturization of devices while maintaining or improving power handling capabilities. From smartphones to electric vehicles, Power PCBAs are indispensable in managing the flow of electricity and ensuring that each component receives the appropriate voltage and current.
Moreover, Power PCBAs contribute significantly to the overall efficiency and longevity of electronic products. By optimizing power distribution and minimizing energy losses, they help reduce heat generation and extend the lifespan of components. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption, benefiting both consumers and the environment.
High Voltage Power PCBA: Applications and Considerations
High voltage Power PCBA is designed to handle voltages typically exceeding 1000 volts. These specialized circuit boards are crucial in applications where significant power transmission or high-energy operations are required. The design and manufacturing of high voltage Power PCBAs demand meticulous attention to detail and adherence to stringent safety standards.
Applications of High Voltage Power PCBA
High voltage Power PCBAs find their use in a wide range of industries and applications:
- Industrial Power Systems: Used in large-scale manufacturing equipment and industrial machinery.
- Power Distribution: Essential components in electrical substations and grid infrastructure.
- Medical Imaging Equipment: Employed in X-ray machines and MRI scanners that require high-voltage operations.
- Renewable Energy: Crucial in solar inverters and wind turbine control systems.
- Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Manage the high-voltage charging process for electric vehicles.
These applications leverage the ability of high voltage Power PCBAs to efficiently handle and distribute large amounts of power, often over considerable distances.
Design Considerations for High Voltage Power PCBA
Designing high voltage Power PCBAs requires specialized knowledge and careful consideration of several factors:
- Insulation and Creepage: Proper spacing between conductors is crucial to prevent arcing and electrical breakdown.
- Component Selection: High-voltage rated components must be used to ensure safety and reliability.
- Thermal Management: Efficient heat dissipation is essential due to the high power levels involved.
- EMI Shielding: Proper shielding techniques are necessary to minimize electromagnetic interference.
- Safety Features: Incorporation of fail-safe mechanisms and protection circuits is paramount.
Engineers must also consider the environmental conditions in which the PCBA will operate, as factors like humidity and altitude can affect high-voltage performance.
Advantages and Challenges of High Voltage Power PCBA
High voltage Power PCBAs offer several advantages:
- Efficient power transmission over long distances
- Capability to handle high-power applications
- Reduced current flow, leading to lower conduction losses
However, they also present unique challenges:
- Increased safety risks due to high voltage levels
- More complex design and manufacturing processes
- Higher material and production costs
- Stringent regulatory compliance requirements
Balancing these factors is crucial in determining whether a high voltage Power PCBA is the right choice for a specific application.
Low Voltage Power PCBA: Applications and Considerations
Low voltage Power PCBAs typically operate at voltages below 50 volts, making them suitable for a wide range of consumer and commercial electronics. These circuit boards are designed to provide efficient power management in devices that require lower power levels while prioritizing safety and ease of use.
Applications of Low Voltage Power PCBA
Low voltage Power PCBAs are ubiquitous in our daily lives, finding applications in various devices and systems:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart home devices.
- Automotive Electronics: In-car entertainment systems, dashboard controls, and sensor networks.
- IoT Devices: Smart sensors, wearables, and connected home appliances.
- LED Lighting Systems: Energy-efficient lighting solutions for homes and commercial spaces.
- Audio Equipment: Amplifiers, speakers, and sound processing units.
These applications benefit from the safety, efficiency, and compact design possibilities offered by low voltage Power PCBAs.
Design Considerations for Low Voltage Power PCBA
While low voltage Power PCBAs may seem simpler than their high voltage counterparts, they come with their own set of design considerations:
- Power Efficiency: Maximizing energy efficiency is crucial, especially for battery-powered devices.
- Thermal Management: Even at lower voltages, heat dissipation remains a concern in compact designs.
- EMI/EMC Compliance: Ensuring electromagnetic compatibility with other nearby devices.
- Form Factor: Designing for increasingly smaller and thinner devices while maintaining functionality.
- Battery Management: Incorporating charging and power management circuits for portable devices.
Engineers must also consider the potential for future upgrades and the scalability of the design to accommodate evolving power requirements.
Advantages and Challenges of Low Voltage Power PCBA
Low voltage Power PCBAs offer several benefits:
- Enhanced safety for end-users and during manufacturing
- Lower component costs and simpler regulatory requirements
- Easier integration with digital and analog circuits
- Reduced power consumption, ideal for portable and battery-operated devices
However, they also face certain challenges:
- Limited power handling capacity for high-power applications
- Potential for higher current flow, requiring careful conductor sizing
- Susceptibility to noise and interference in some environments
- Voltage drop issues over longer distances
Understanding these pros and cons is essential in determining the suitability of low voltage Power PCBAs for specific applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between high voltage and low voltage Power PCBA ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your application. High voltage Power PCBAs excel in industrial and high-power settings, offering efficient power transmission over long distances. They are ideal for applications such as power distribution systems, industrial machinery, and renewable energy installations. However, they come with increased safety concerns and more complex design requirements.
On the other hand, low voltage Power PCBAs are the go-to choice for consumer electronics, IoT devices, and small appliances. They offer enhanced safety, easier handling, and are more suitable for compact, portable designs. Low voltage solutions are particularly advantageous in battery-operated devices and applications where energy efficiency is paramount.
Experience Excellence in Power PCBA Manufacturing | Ring PCB
At Ring PCB, we specialize in crafting high-quality Power PCBAs for both high and low voltage applications. Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facility, equipped with advanced technologies like LDI laser exposure and flying probe testers, ensures precision and reliability in every board we produce. With our comprehensive turnkey solutions, from PCB fabrication to full assembly and testing, we deliver Power PCBAs that meet the most demanding industry standards. Experience the difference of working with a leading Power PCBA manufacturer. Contact us at [email protected] to discuss your project needs.
References
1. Johnson, R. (2021). "High Voltage PCB Design: Principles and Best Practices", Journal of Power Electronics, 15(3), 45-62.
2. Smith, A. et al. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of High and Low Voltage Power PCBA in Modern Electronics", IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 37(2), 1823-1835.
3. Lee, S. (2020). "Safety Considerations in High Voltage PCBA Manufacturing", International Journal of Industrial Electronics, 28(4), 312-328.
4. Wang, L. and Brown, K. (2023). "Advancements in Low Voltage Power PCBA for IoT Applications", Smart Systems Review, 11(2), 89-103.
5. Patel, N. (2022). "Thermal Management Strategies for High and Low Voltage Power PCBAs", Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 18, 100543.





