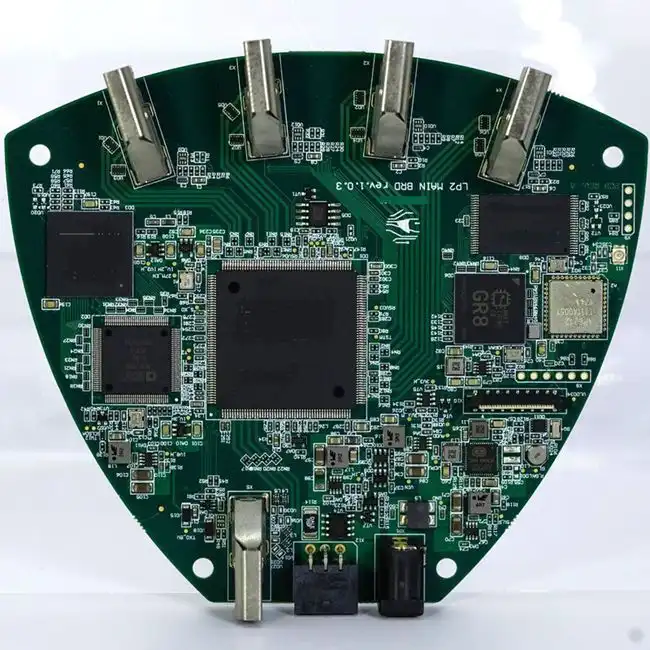
Understanding the PCB Assembly Process
The Journey from PCB to PCBA
The transformation of a PCB into a PCBA is a sophisticated process that requires precision and expertise. It begins with the bare PCB, which serves as the foundation for the electronic components. The PCB Assembly process involves several key steps:
- Solder Paste Application: A thin layer of solder paste is applied to the PCB's surface using a stencil.
- Component Placement: Automated machines precisely place components onto the board.
- Reflow Soldering: The board is heated to melt the solder paste, securing the components in place.
- Inspection and Testing: Quality control measures ensure proper assembly and functionality.
Each stage of the PCB Assembly process is crucial for creating a high-quality, reliable electronic product. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as surface-mount technology (SMT), have revolutionized the assembly process, allowing for more compact and efficient designs.
The Role of Automation in PCBA
Automation plays a pivotal role in modern PCB Assembly. State-of-the-art pick-and-place machines can place thousands of components per hour with incredible accuracy. This level of precision and speed is essential for meeting the demands of complex electronic designs and high-volume production.
Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems and X-ray inspection tools are also integral to the PCBA process. These technologies can detect issues such as misaligned components, solder bridges, or insufficient solder joints that might be invisible to the human eye. By incorporating these advanced quality control measures, manufacturers can significantly reduce defect rates and ensure the reliability of the final product.
Key Differences Between PCB and PCBA
Functionality and Complexity
The primary distinction between a PCB and a PCB Assembly lies in their functionality and complexity. A PCB is essentially a blank canvas – it provides the conductive pathways for electrical signals but cannot perform any functions on its own. In contrast, a PCBA is a fully functional electronic circuit, capable of carrying out specific tasks based on its design and components.
PCBAs can vary greatly in complexity, from simple single-layer boards with a few components to multi-layer boards with hundreds or even thousands of components. The complexity of a PCBA is determined by factors such as:
- The number and types of components used
- The density of the component placement
- The number of layers in the PCB
- The specific requirements of the end application
As electronic devices become more sophisticated, the complexity of PCBAs continues to increase, pushing the boundaries of manufacturing capabilities and design innovation.
Manufacturing Processes and Costs
The manufacturing processes for PCBs and PCBAs differ significantly, which impacts their respective costs. PCB production involves creating the bare board with its conductive tracks and pads. This process includes:
- Designing the circuit layout
- Etching the copper layers
- Drilling holes for vias and component leads
- Applying solder mask and silkscreen
PCB Assembly manufacturing builds upon the PCB production process by adding the component assembly stage. This additional step involves:
- Sourcing and managing inventory of electronic components
- Precise placement and soldering of components
- Multiple stages of testing and quality control
Due to the additional processes and materials involved, PCBA production is generally more expensive than PCB production alone. However, the cost per unit can be significantly reduced through economies of scale in high-volume production runs.
The Importance of Quality Control in PCB Assembly
Ensuring Reliability and Performance
Quality control is paramount in PCB Assembly to ensure the reliability and performance of the final product. Rigorous testing procedures are implemented throughout the assembly process to identify and rectify any issues before the PCBA reaches the end-user. Some key quality control measures include:
- In-Circuit Testing (ICT): Verifies the electrical integrity of the assembled board
- Functional Testing: Ensures the PCBA performs its intended functions correctly
- Environmental Stress Screening: Subjects the PCBA to various environmental conditions to detect potential weaknesses
- Burn-In Testing: Operates the PCBA under stress conditions to identify early-life failures
These quality control processes are essential for industries that rely on high-reliability electronics, such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive applications. By implementing thorough quality control measures, manufacturers can minimize the risk of field failures and ensure customer satisfaction.
The Role of Industry Standards
PCB Assembly is governed by various industry standards that ensure consistency and quality across manufacturers. These standards, such as those set by the IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits), provide guidelines for:
- PCB design and manufacturing
- Component selection and placement
- Soldering techniques and quality
- Testing and inspection procedures
Adherence to these standards is crucial for producing high-quality PCBAs that meet the rigorous requirements of modern electronic devices. Manufacturers that consistently meet or exceed these standards are often preferred by OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) for their reliability and quality assurance.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between PCB and PCBA is crucial for anyone involved in electronics design or manufacturing. While a PCB provides the foundation, it's the PCB Assembly process that brings electronic circuits to life. The complexity of modern electronics demands precision, reliability, and quality at every stage of production.
For businesses seeking a trusted PCB Assembly supplier or manufacturer, it's essential to partner with a company that demonstrates expertise in both PCB fabrication and assembly. Look for suppliers who offer comprehensive PCBA services, adhere to industry standards, and employ rigorous quality control measures. By choosing the right PCBA manufacturer, you can ensure that your electronic products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
FAQ
What are the main advantages of PCBA over PCB?
PCBA offers a complete, functional circuit ready for use, while PCB is just the bare board. PCBA includes all necessary components, reducing assembly time for end-users.
How long does the PCB Assembly process typically take?
The duration varies based on complexity and volume, but can range from a few hours for simple boards to several days for complex, high-volume production runs.
Are there environmental considerations in PCB Assembly?
Yes, many manufacturers now use lead-free solder and comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) standards to minimize environmental impact.
Experience Precision and Quality in PCB Assembly | Ring PCB
At Ring PCB, we leverage our advanced engineering capabilities to deliver top-tier PCB Assembly services. Our state-of-the-art facility, equipped with high-density stack-up technology and smart manufacturing processes, ensures precision in every PCBA we produce. From 2-48 layer boards to tight trace/spacing requirements, we meet the exacting needs of industries ranging from 5G to automotive electronics. Trust our expert team for comprehensive, one-stop PCBA solutions that prioritize quality and efficiency. Contact us at [email protected] to experience the difference of working with a leading PCB Assembly manufacturer and supplier.