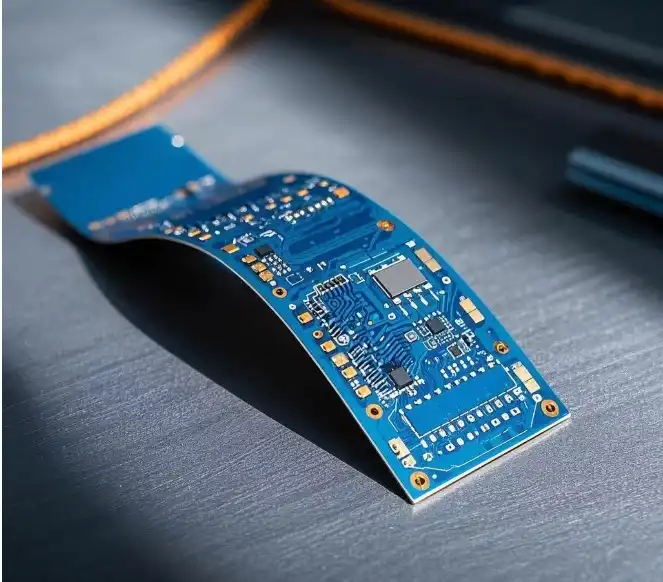
Comprehending the Fundamental Differences Between Flex and Rigid PCBs
To make an informed decision between flex and rigid PCBs for your prototype, it's crucial to grasp their fundamental differences. Flex PCBs, as the name suggests, are flexible circuit boards that can bend and conform to various shapes. They are constructed using thin, pliable materials like polyimide or polyester films. This flexibility allows them to be folded, twisted, or shaped to fit into tight or unconventional spaces.
On the other hand, rigid PCBs are the traditional, inflexible circuit boards that most people are familiar with. They are typically made from a solid substrate material like FR-4 (a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate). Rigid PCBs provide a stable platform for mounting components and are well-suited for applications that require structural integrity.
Key Characteristics of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs offer several unique advantages that make them attractive for certain prototype applications:
- Flexibility: The ability to bend and conform to various shapes is the primary characteristic of flex PCBs.
- Space-saving: Their thin profile and ability to fold allow for more compact designs.
- Weight reduction: Flex PCBs are typically lighter than their rigid counterparts.
- Dynamic applications: They can withstand repeated bending or flexing, making them suitable for moving parts.
- 3D packaging: Flex PCBs enable innovative 3D circuit designs that are impossible with rigid boards.
Key Characteristics of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs have their own set of advantages that make them the preferred choice for many applications:
- Stability: They provide a solid, unchanging platform for component mounting.
- Durability: Rigid PCBs can generally withstand more physical stress and environmental factors.
- Cost-effectiveness: For simple, straightforward designs, rigid PCBs are often more economical.
- Heat dissipation: The solid substrate of rigid PCBs often provides better heat dissipation.
- Ease of manufacturing: Rigid PCBs are typically easier and faster to produce in large quantities.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Flex and Rigid PCBs for Prototypes
When deciding between flex and rigid PCBs for your prototype, several factors come into play. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on your specific project requirements.
Space Constraints and Form Factor
One of the primary considerations is the available space and the desired form factor of your prototype. If you're working with tight spaces or need to fit your PCB into an unconventional shape, a flex PCB might be the better option. Flex PCBs can be folded or bent to conform to the available space, allowing for more compact designs. This makes them particularly useful in applications like wearable technology, mobile devices, or any product where space is at a premium.
Rigid PCBs, while less versatile in terms of shape, are still the go-to choice for many applications where space isn't a significant constraint. They're ideal for flat, open spaces and can be easily stacked or mounted in standard enclosures.
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which your prototype will operate is another crucial factor. Flex PCBs have a natural advantage in environments with vibration or movement, as their flexibility allows them to absorb shock and resist damage from mechanical stress. They're also well-suited for applications that involve repeated bending or flexing.
However, rigid PCBs often have the upper hand when it comes to harsh environments. Their solid construction makes them more resistant to extreme temperatures, humidity, and chemical exposure. If your prototype needs to withstand tough environmental conditions, a rigid PCB might be the safer choice.
Production Volume and Cost Considerations
When it comes to prototyping, cost is often a significant factor. In general, rigid PCBs are more cost-effective for low to medium volume production. They're easier to manufacture and assemble, which translates to lower production costs. Flex PCBs, while offering unique advantages, are typically more expensive to produce, especially in small quantities.
However, it's important to consider the long-term costs as well. While flex PCBs might have a higher upfront cost, their ability to fit into smaller spaces or eliminate the need for multiple rigid boards can sometimes lead to overall cost savings in the final product design.
Practical Applications and Case Studies: When to Use Flex vs. Rigid PCBs?
To further illustrate when to choose flex or rigid PCBs for prototypes, let's explore some practical applications and case studies. These real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the decision-making process.
Flex PCB Applications
Flex PCBs shine in applications where space is limited, weight is a concern, or flexibility is required. Here are some examples:
- Wearable Technology: Smartwatches and fitness trackers often use flex PCBs to conform to the curved surfaces of the wrist.
- Aerospace: Flex PCBs are used in satellites and aircraft to save weight and fit into tight spaces.
- Medical Devices: Implantable medical devices benefit from the small size and flexibility of flex PCBs.
- Automotive: Modern vehicles use flex PCBs in dashboard displays and other areas where space is constrained.
Case Study: A startup developing a new smartwatch prototype chose a flex PCB for their initial design. The flex PCB allowed them to create a curved circuit board that fit perfectly within the watch's rounded case, maximizing the space for other components like the battery and display. The flexibility of the PCB also provided better resistance to the constant movement and vibration a watch experiences.
Rigid PCB Applications
Rigid PCBs are the workhorses of the electronics world, suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Computer Hardware: Motherboards, graphics cards, and other computer components typically use rigid PCBs.
- Industrial Control Systems: Rigid PCBs provide the durability needed in harsh industrial environments.
- Consumer Electronics: Many household appliances and gadgets use rigid PCBs for their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
- Telecommunications: Cell towers and networking equipment often rely on rigid PCBs for their stability and ability to handle high-frequency signals.
Case Study: An engineering team prototyping a new industrial control panel opted for a rigid PCB design instead of a flex PCB. The panel needed to withstand high temperatures and potential exposure to chemicals in the factory environment. The rigid PCB's durability and heat dissipation properties made it the ideal choice. Additionally, the lower production cost of rigid PCBs allowed the team to produce multiple prototype iterations within their budget constraints.
Hybrid Approaches
In some cases, the best solution might be a combination of flex and rigid PCBs. These hybrid designs, often called rigid-flex PCBs, combine the benefits of both types:
- Cameras: Digital cameras often use rigid-flex PCBs to connect the lens assembly to the main circuit board.
- Military Equipment: Ruggedized devices for military use can benefit from the durability of rigid sections combined with the flexibility of flex sections.
Case Study: A team developing a prototype for a compact, high-performance drone used a rigid-flex PCB design. The rigid sections provided stability for sensitive components and helped with heat dissipation, while the flex sections allowed the circuitry to fit within the drone's small, curved body. This hybrid approach enabled the team to maximize the drone's capabilities while minimizing its size and weight.
Conclusion
Choosing between flex and rigid PCBs for prototypes is a nuanced decision that depends on various factors. Flex PCBs offer unparalleled flexibility, space-saving capabilities, and are ideal for dynamic applications. They excel in scenarios where conformity to unique shapes or repeated bending is necessary. However, they come with higher production costs, especially for small quantities.
Rigid PCBs, on the other hand, provide stability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. They are the go-to choice for applications requiring structural integrity, better heat dissipation, and resistance to harsh environments. Their ease of manufacturing also makes them more economical for many prototype projects.
In some cases, a hybrid approach using rigid-flex PCBs can provide the best of both worlds. Ultimately, the choice between flex and rigid PCBs should be guided by your project's specific requirements, including space constraints, environmental conditions, production volume, and budget considerations.
As technology continues to evolve, both flex and rigid PCBs will undoubtedly play crucial roles in the development of innovative prototypes across various industries. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each type, you can make an informed decision that best serves your prototype's needs and sets the foundation for a successful final product.
FAQ
Can flex PCBs handle high-frequency signals as well as rigid PCBs?
While rigid PCBs generally perform better with high-frequency signals, advancements in flex PCB technology have improved their high-frequency capabilities. However, for critical high-frequency applications, rigid PCBs are often preferred.
Are flex PCBs more prone to damage than rigid PCBs?
Flex PCBs are designed to withstand bending and flexing, but they can be more sensitive to certain types of damage, such as sharp creases. Rigid PCBs are generally more robust against physical impacts.
Can I use the same design for both flex and rigid PCBs?
While some design principles are shared, flex PCBs often require specific design considerations to account for their unique properties. It's best to consult with a PCB manufacturer for guidance on translating designs between flex and rigid PCBs.
Expert PCB Prototyping Solutions for Your Flex and Rigid PCB Needs | Ring PCB
At Ring PCB, we excel in providing top-notch prototyping solutions for both flex and rigid PCBs. Our team of over 500 professionals brings extensive expertise to every project, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. With our advanced R&D capabilities, 24/7 customer support, and ISO-certified quality control, we deliver innovative and reliable PCB solutions tailored to your specific needs. For expert guidance on your prototype PCB requirements, contact our experienced team at [email protected].
References
1. Johnson, M. (2021). "Flex vs. Rigid PCBs: A Comprehensive Comparison for Prototype Design". Journal of Electronics Manufacturing, 15(3), 78-92.
2. Smith, A. and Brown, J. (2020). "Advancements in Flexible Circuit Technology for Modern Prototyping". IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology, 10(2), 245-260.
3. Lee, S. et al. (2019). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Flex and Rigid PCBs in Prototype Development". International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 7(4), 112-125.
4. Garcia, R. (2022). "Environmental Considerations in PCB Selection for Prototypes". Sustainability in Electronics Design, 8(1), 35-50.
5. Patel, K. and Wilson, T. (2020). "Case Studies in PCB Prototyping: Lessons from Industry Leaders". Prototype Engineering Quarterly, 12(2), 67-82.